Hi Fellas,
I want to share something about Site of Origin Issue.
So Basicly What is Site of Origin ?? ;
It is used for more focused on loop prevention for multihomed MPLS customers.
( we can use BGP Cost Community instead, I will share it later...)
CE Routers are connected to PE also they have a back-up link between of them that is we called multihomed in this case.
LOOP !!!!
For clarity, lets diagram this ;
PE advertise routes, and somehow ;
Routes reach CE-R10 towards R8 before going directly CE-R8. When R8 learns about R4's routes from CE-R10, it doesn't install the routes. Instead, from then on it; it prefers to go the " long way around" via PE-R6 and CE -R10
L
O
O
P
!
!
Example ;
CE1 send out the routes, somehow PE1 gets them first before CE2 through backup-link . PE1 at this point sets SOO 1:1 on the EIGRP route then it goes to PE3 > PE2 , PE2 accepts this route because SOO 1:1 different than SOO 2:2.
Even CE2 is try to re-advertise routes to CE1 ( which is advertised by CE1 ), CE1 won't accept the routes because 1:1 won't let the same ID going in.
Note that;
PE2 does not re-write the tag from 1:1 to 2:2. Tags are only written if they are missing, they are never re-written.
I configure SOO 1:1 on Site A , SOO 2:2 on Site B ;
Routes leave site A will be tagged with 1:1 and routes leave site B will be tagged with 2:2
Site a will accept Site B2s routes and Site B will accept Site A's routes , but Site A won't accept it's own routes back in on the "border" routers.
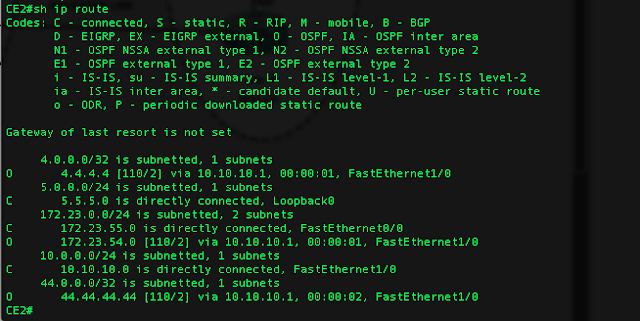
The network connection seems ok, CE1 can ping CE2's loopback address (Backdoor link is shutdown for testing purpose only that MPLS works)
And we see 5.5.5.0/24 prefix next hop address is 10.10.10.2 which uses through backdoor link !
PE1
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip address 172.23.54.15 255.255.255.0
delay 100
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface FastEthernet1/0
bandwidth 100
ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.0
delay 10000000
duplex auto
speed auto
!
I change default delay settings that CE1 prefixes (for 5.5.5.0/24 ) is forwarded to PE1 instead of backdoorlink.
And as I mentioned before, that could create loop for our MPLS network grid. ! We will use SOO ;
PE 1
route-map SOOx permit 10
set extcommunity soo 1:1
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
ip vrf forwarding asd
ip vrf sitemap SOOx
ip address 172.23.54.16 255.255.255.0
duplex auto
speed auto
So0 is 1:1 now :) No worries for loop issue again :D