Lets put some spice on classic MPLS cliche design with Route Reflectors.
If we are lucky, 3 or 4 IBGP router peering is nothing when we try to configure I-BGP peering ;full mesh. But If we don't....
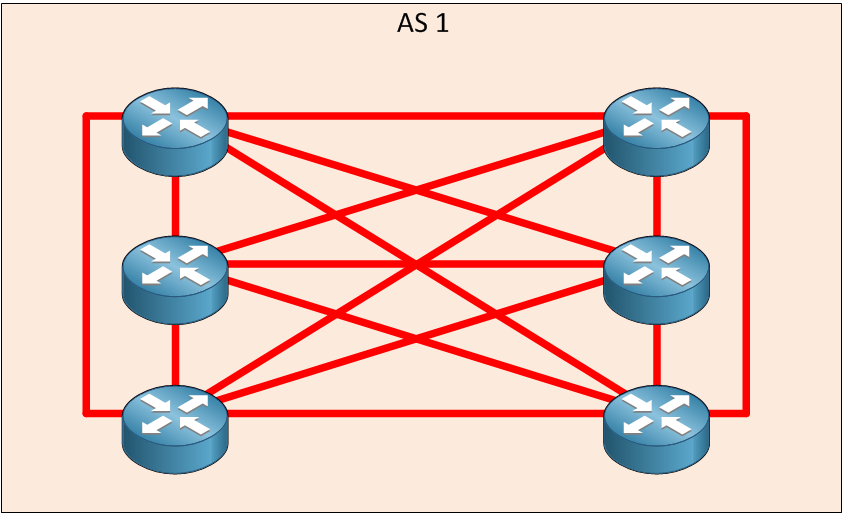
In BGP, updates received by a peer in an AS are not allowed to be forwarded to another peer within the same AS.
That's why we need to use full-mesh to make neighbor each IBGP Router.
We need to determine n*(n-1)/2 peerings in IBGP domain... This is sucks when we have more than at least 5 routers 5*4/2 = 10 peerings !!!!!
PS: IBGP Routers do not need to directly connected like EIGRP or OSPF. !
PS2 : When a prefix is learned by another IBGP router ; the advertised prefix's next-hop address remains the same. Against that problem we can use these:
- Next-hop-self command or
-Advertise prefixes
Otherwise;
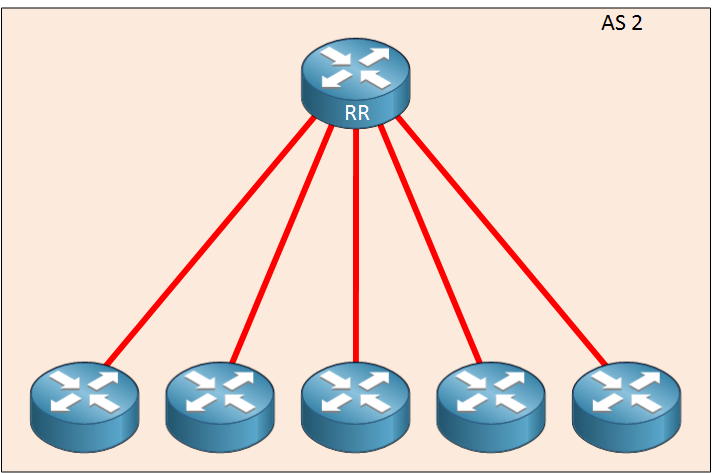
When you configure a route reflector you have to tell the router whether the other IBGP router is a client or non-client. A client is an IBGP router that the route reflector will “reflect” routes to, the non-client is just a regular IBGP neighbor.
A route reflector is BGP router that is allowed to break the iBGP loop avoidance rule. Route reflectors can advertise updates received from an iBGP peer to another iBGP peer under specific conditions.
- A route learned from an EBGP neighbor can be forwarded to another EBGP neighbor, a client and non-client.
- A route learned from a client can be forwarded to another EBGP neighbor, client and non-client.
- A route learned from a non-client can be forwarded to another EBGP neighbor and client, but not to a non-client.
Client: Will be reflect routes comes from others. (like HQ or Hub or something :) )
Non-Client : Will act like a regular IGBP router.
- Any updates would be sent to the RR alone.
- The RRs are then responsible for propagating information received from PEs to all other PEs.
- Each time a PE is added, a neighbor statement pointing to the RR needs to be added on the new PE router, and on the RR, a neighbor statement pointing to the PE must be added.
Route-Reflector-Client with Layer 3 VPN :
Customer A (R5-R6) contains IGP AS 51 Area 1
Provider Site : BG1 , OSPF 100 Area0
VPN Connection PE ; Router Ospf 50 Area 1
R1(config)#int fa0/0
R1(config-if)#ip os 1 ar 0
R1(config-if)#mpls ip
R1(config-if)#int fa0/1
R1(config-if)#ip os 1 ar 0
R1(config-if)#mpls ip
R1(config-if)#int lo 0
R1(config-if)#int lo 0
R1(config-if)#ip os 1 ar 0
R1(config-if)#exit
R2(config)#int fa0/0
R2(config-if)#ip os 1 ar 0
R2(config-if)#mpls ip
R2(config-if)#int fa0/1
R2(config-if)#ip os 1 ar 0
R2(config-if)#mpls ip
R2(config-if)#int lo0
R2(config-if)#int lo0
R2(config-if)#ip os 1 ar 0
R2(config-if)#exit
R3(config)#int fa0/0
R3(config-if)#ip os 1 ar 0
R3(config-if)#mpls ip
R3(config-if)#int fa0/1
R3(config-if)#ip os 1 ar 0
R3(config-if)#mpls ip
R3(config-if)#int lo0
R3(config-if)#ip os 1 ar 0
R3(config-if)#exit
R4(config)#int fa0/0
R4(config-if)#ip os 1 ar 0
R4(config-if)#mpls ip
R4(config-if)#int fa0/1
R4(config-if)#ip os 1 ar 0
R4(config-if)#mpls ip
R4(config-if)#int lo0
R4(config-if)#ip os 1 ar 0
R4(config-if)#exit
R3(config)#ip vrf Cust_A
R3(config-vrf)# description Customer-A
R3(config-vrf)# rd 1:100
R3(config-vrf)# route-target export 1:100
R3(config-vrf)# route-target import 1:100
R3(config-vrf)#exit
R3(config)#int fa1/0
R3(config-if)#ip vrf forwarding Cust_A
R4(config)#ip vrf Cust_A
R4(config-vrf)# description Customer-A
R4(config-vrf)# rd 1:100
R4(config-vrf)# route-target export 1:100
R4(config-vrf)# route-target import 1:100
R4(config-vrf)#exit
PE2(config)#int fa1/0
PE2(config-if)#ip vrf forwarding Cust_A
PE2(config-if)#exit
R3(config)#router ospf 50 vrf Cust_A
R3(config-router)# log-adjacency-changes
R3(config-router)# network 172.23.54.0 0.0.0.255 area1
R3(config-router)#exit
R4(config)#router ospf 100 vrf Cust_A
R4(config-router)# log-adjacency-changes
R4(config-router)# network 172.23.53.0 0.0.0.255 area 1
R4(config-router)#exit
R5(config)#int lo 0
R5(config-if)# ip ospf 51 area 1
R5(config-if)#int fa0/0
R5(config-if)# ip ospf 51 area 1
R5(config-if)#exit
R6(config)#int lo 0
R6(config-if)# ip ospf 51 area 1
R6(config-if)#int fa0/0
R6(config-if)# ip ospf 51 area 1
R6(config-if)#exit
R3(config)#router ospf 50 vrf Cust_A
R3(config-router)# redistribute bgp 1 subnets
R3(config-router)#exit
R3(config)#router bgp 1
R3(config-router)#address-family ipv4 vrf Cust_A
R3(config-router-af)#redistribute os 50 vrf Cust_A
R4(config)#router ospf 50 vrf Cust_A
R4(config-router)# redistribute bgp 1 subnets
R4(config-router)#exit
R4(config)#router bgp 1
R4(config-router)#address-family ipv4 vrf Cust_A
R4(config-router-af)#redistribute os 50 vrf Cust_A
R3(config)#router bgp 1
R3(config-router)# neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 1
R3(config-router)# neighbor 2.2.2.2 update-source Loopback0
R3(config-router)# neighbor 3.3.3.3 remote-as 1
R3(config-router)# neighbor 3.3.3.3 update-source Loopback0
R3config-router)# address-family vpnv4
R3(config-router-af)# neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
R3(config-router-af)# neighbor 2.2.2.2 send-community both
R3(config-router-af)# neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
R3(config-router-af)# neighbor 3.3.3.3 send-community both
R3(config-router-af)# exit-address-family
R3(config-router)#exit
R4(config)#router bgp 1
R4(config-router)# neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 1
R4(config-router)# neighbor 2.2.2.2 update-source Loopback0
R4(config-router)# neighbor 3.3.3.3 remote-as 1
R4config-router)# neighbor 3.3.3.3 update-source Loopback0
R4(config-router)# address-family vpnv4
R4(config-router-af)# neighbor 2.2.2.2 activate
R4(config-router-af)# neighbor 2.2.2.2 send-community both
R4(config-router-af)# neighbor 3.3.3.3 activate
R4(config-router-af)# neighbor 3.3.3.3 send-community both
R4(config-router-af)# exit-address-family
R4(config-router)#exit
R3(config)#router bgp 1
R3(config-router)#neighbor RR1 peer-group
R3(config-router)#neighbor RR1 remote-as 1
R3(config-router)#address-family vpnv4
R3(config-router-af)#neighbor 4.4.4.4 peer-group RR1
R3(config-router-af)#neighbor 5.5.5.5 peer-group RR1
R3(config-router-af)#neighbor RR1 route-reflector-client
R3(config-router-af)#end
R4(config)#router bgp 1
R4(config-router)#neighbor RR2 peer-group
R4(config-router)#neighbor RR2 remote-as 1
R4(config-router)#address-family vpnv4
R4(config-router-af)#neighbor 4.4.4.4 peer-group RR2
R4(config-router-af)#neighbor 5.5.5.5 peer-group RR2
R4(config-router-af)#neighbor RR2 route-reflector-client
R4(config-router-af)#end



